The modern world is undergoing an energy transformation and at the center of it, is the smart grid, a sophisticated system redefining how we produce, distribute, and consume electricity. Unlike the traditional grid, which has remained largely unchanged for decades, the smart grid leverages digital technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) to build a dynamic, efficient, and more sustainable energy network.
What is a Smart Grid?
A smart grid is an advanced electricity distribution system that combines real-time monitoring, automated control, and digital communication tools to improve energy efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. Using components like smart meters, sensors, AI algorithms, and two-way communication systems, smart grids allow both utilities and consumers to track energy usage and adapt to shifting demands in real time.
When a disruption such as a power outage occurs, smart grids can automatically reroute electricity, minimizing downtime and maintaining service. This capability makes the grid more resilient. Furthermore, smart grids are designed to support renewable energy integration, balancing variable inputs from solar or wind with consumer needs.
How Smart Grids Work
Smart grids rely on a connected system of hardware and software to collect, analyze, and act on data. The combination of real-time monitoring, modern distribution systems, and data analytics creates a robust framework for smart grids as follows.
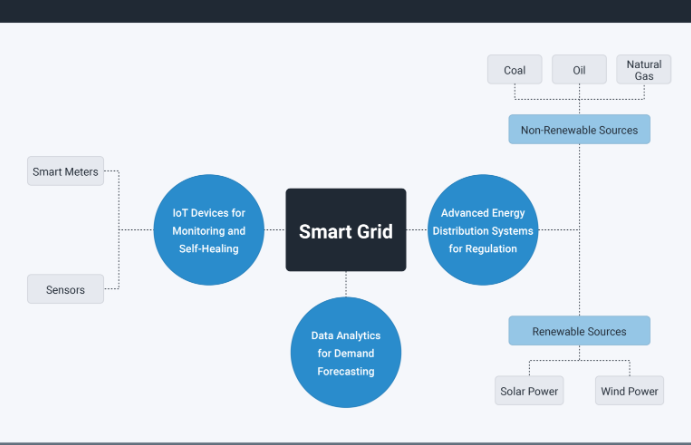
Key Components Include
Real-Time Monitoring & Control
Sensors and smart meters track electricity flow, allowing utilities to detect anomalies, manage demand, and respond immediately to issues.
Data Analytics and AI
AI-powered analytics process usage data, forecast demand, and identify potential failures before they happen—ensuring proactive maintenance and system reliability.
Advanced Distribution System
Smart grids manage power from multiple sources including solar, wind, and traditional plants balancing supply with real-time demand for maximum efficiency.
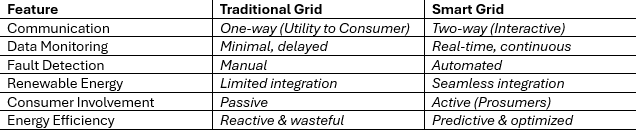
Smart Grid vs Traditional Grid: What’s the Difference?
Benefits of Smart Grids
Improved Energy Efficiency
With real-time data, users can adjust consumption to avoid peak-time charges, while utilities fine-tune energy production to avoid waste.
Enhanced Reliability
Smart grids quickly detect and isolate faults, often rerouting power without human intervention. This reduces blackouts and boosts uptime.
Better Renewable Integration
Smart grids help balance the variable supply from solar and wind, enabling a cleaner energy mix and allowing consumers to sell back excess energy.
Cost Reduction & Emissions Control
Efficient operation and support for renewables lower costs for both utilities and consumers while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges in Smart Grid Adoption
Despite its many advantages, implementing smart grid technology isn’t without hurdles:
High Infrastructure Costs
Initial investment in smart meters, sensors, and communication tools can be expensive. Public-private partnerships and phased rollouts can ease the financial burden.
Cybersecurity & Privacy
More data means greater exposure. Utilities must invest in cybersecurity and build public trust through transparent data policies.
Technical Complexity
Integrating different devices and standards poses challenges. Industry collaboration and standardization are key to ensuring system compatibility.
Consumer Awareness
Lack of understanding and engagement can stall progress. Educational initiatives and incentives can help consumers adopt smarter energy habits.